Just Tell us Your Idea, Zetar Can Make It Come True.
From Injection Mold to Plastic Product
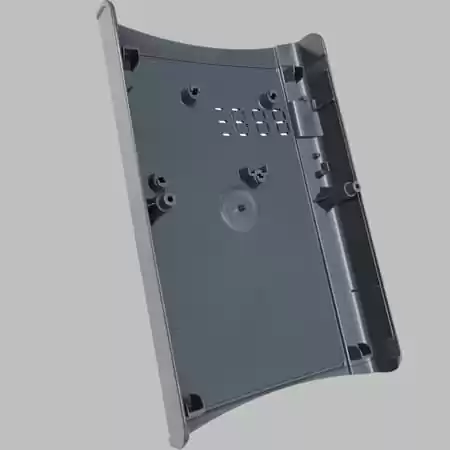


Plastic Injection Molding Services
- Zetar grown up in the industry applying a hands on approach to precision injection molding. We offer complete project management services that leverage our years of experience manufacturing products for a wide array of applications. This vast knowledge base allows us to make materials selection, facilitate parts sourcing, as well as complete product development.
- Strong Production Capacity-Now total we have 31 sets injection machines which 6 sets are in dust-free room (M7 Class) for FDA products and medical products. The largest 1100T machine could produce product weight up to 5100g.
Injection Molding Process Flowchart

Order
When Ordering is confirmed, information is gathered

Working Schedule
Machine scheduling, post-processing, assembly, packaging and logistics planning

Material Purchasing
Procurement staff acts as an inspector for material purchasing

Data Setting
Date is set for the first production

Injection Mould Set Up
Injection Mould tool is set on the machine

Granular Plastic Processing
Granular plastic is fed by gravity from a hopper into a heated barrel

First Production Checking
First Injection molding Production is made and the quality is assured

Mass Production
Plastic injection molding product are made with high standard

Quality Control
Our CMM checks plastic injection molding product quality

Delivery
Plastic injection molding products are packed and delivered on-time

Warehousing
Plastic injection molding products are stored in warehouse

Packing
Plastic injection molding product is packed as client required
Injection Molding: What You Need to Know
In this blog post we will discuss what injection molding is, how it works, some advantages and disadvantages associated with it, as well as provide some information on how you can use injection molding technology in your manufacturing processes!
Table Of Contents
What is injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that allows manufacturers to produce plastic and other types of parts in large quantities. It has been around for over 100 years and has contributed greatly to the advancement of our society in terms of both convenience and quality.
It was developed to replace other traditional manufacturing processes, such as casting and cnc machining, which were both slower and more expensive. In injection moulding, molten thermoplastic material is injected into a closed cavity or mold under high pressure of plastic injection molding machines.
The plastic material cools upon contact with the mold walls and hardens over time before being removed from the mold to produce a injection molded part with desired physical properties.

How does it Work?
- The first stage of injection molding is to create the injection molding tool itself. Most mold tools are made from metal, usually aluminium or steel. They must be precision-machined to extremely tight tolerances in order to ensure a good fit for the plastic injection molded parts that will be injected. The injection mold is also designed with cooling channels in order to allow the molten plastic to cool and harden quickly after it has been injected into the injection mold tool.
- Once the injection mold is created, the second stage is to inject the molten plastic material into it. This is done using a high-pressure injection molding machine. The machine forces the molten plastic into the cavity or injection mold under high pressure, where it quickly cools and hardens, matching the shape of the mould.
- The cooling time can be reduced through the use of cooling lines that circulate water or oil from an external temperature controller. This will help to speed up the process and ensure that the molten plastic is cooled and hardened properly.
- Mold tool is mounted on plate moulds, which open once the material has solidified so that ejector pins can eject the part from the injection molding tool. This process is usually done using an air cylinder or hydraulic ram, which pushes the ejector pins out of the mould and forces the plastic part to be ejected.
- Moulds can be made of single cavity tool or multi cavity tool. Multiple cavities metal mold can have identical parts in each cavity or can be unique to create parts of different geometries, such as with products that require "snap-fit" type assembly.

The basic plastic injection molding processes
Injection molding is a process in which hot plastic flows under pressure through an Injection Mold Kit to create plastic components. There are several stages that go into this, such as designing appropriate plastic injection molds for efficient production and careful consideration when analyzing part design with considerations on how it will be injected into the final product; all these make sure you have great results! There are a lot of factors and configurations which we won’t touch on here but the basic process is the same. Let’s start with the basics.
Step 1: Set up mold and close the mold
The Injection Molding cycle timer begins when the injection mold closes. This is the time that the machine takes to inject the plastic into the injection mold and cool it down. The cycle timer ends when the part is ejected from the injection mold.


Step 2: Injection molding process
The injection molding machines force the melted plastic into the injection mold cavity or mold under high pressure. As the melted plastic is injected into this injection mold tool, air bubbles are forced out. These escape through vents in injection pins and along a parting line to prevent excess material from seeping back inside during cooling process
Step 3: Cooling or solidification
After the mold is filled with a liquid plastic material, it’s allowed to cool for an appropriate amount of time. The resin used and thicknesses affect how long this process takes so each type has its own unique cooling system where water cycles through them constantly at just below body temperature in order maintain constant Fahrenheit degrees—that way you can make sure your molds never get too hot or cold!


Step 4: Resin plasticization
The barrel of the machine cools as it retracts, drawing new polymer plastic resin from a hopper. The heater bands maintain this needed temperature for molding different types or resins to ensure proper curing before use.
Step 5: Ejection
As soon as the mold opening, pins move forward and release plastic injection molded parts. Part falls into a bin below waiting for pickup or disposal.The perfect tool to make your day-to-day tasks more enjoyable!

Step 6. Remove the runner and packaging
The plastic injection molding process is not over after the machine cycles through steps 5 and 6. In fact, operators or robots will separate usable plastic from runners for recycling depending on what parts are still needed in one’s product during later stages of production. This can help reduce costs as well as environmental impact by only using necessary waste materials instead going out-of-stock with unnecessary items that would have gone to landfills if they weren’t recycled before being ground up again.
What plastic is used for injection molding?
The plastic material that is used for plastic injection molding is usually a thermoplastic. It’s important to note that there are many different types of common injection molding materials available for injection molding, not all of which are suitable for every application.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is ideal for making products that need an increased level of resilience. These plastic material also show good wear resistance. ABS also offers low shrinkage rates and high dimensional stability.
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
The amazing property of PBT is that it can be used in any application where you need strong, flexible material with high levels resistance to chemicals. It has great electrical properties too making this fiber perfect for power components as well automotive applications!
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a strong, impact-resistant plastic materials that has low shrinkage rates and good dimensional stability. It is ideal for making products that need to be resilient, such as eyeglasses, cell phone cases, and medical devices. A transparent plastic that is available in different optically clear grades, PC can provide a high cosmetic finish and good heat resistance.
Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
PPSU is a material that has been designed with specific properties to withstand high temperatures and extreme conditions with high melting point. It’s also resistant towards most chemicals, meaning it can handle cleaning procedures for long periods without failing or worse yet – releasing harmful substances into your food!
Polypropylene (PP)
Low impact polymers, like polypropylene (PP), are great at manufacturing plastic injection molded parts like tableware (plates, cups, bowls), because they are inexpensive and durable.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
PMMA, the popular choice for applications that require high gloss and scratch resistant material properties. It also has low shrinkage which makes it perfect when working with thin or thick sections in your design!
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a thermoplastic with high hardness, stiffness, strength and toughness. It has a low coefficient of friction and good wear resistance. POM is available in different colors and is good chemical resistance.
Aliphatic Polyamides (PPA)
PPA nylons are a popular choice for those who work with hot liquids. They offer high strength and excellent temperature resistance, as well as being chemically resistant against strong acids or bases in general (although not at the same time). Some types of nylon may also be abrasion resistant which means they resist scratching when dragging across metal surface finish such things like pipes during injection processes for example! These materials often maintain good impact strength so you don’t need to worry about dropping them on purpose
The advantages of injection molding
This process of injection molding helps to produce a high quality and consistent plastic parts. The main advantages of using injection molding are:
- Parts can be made in large quantities mass production
- Parts are consistent in shape and size
- Parts are strong and durable
- Low production costs
The disadvantages of injection molding
Although injection molding is a widely used production process, it does have a few disadvantages.
- The initial cost of setting up an injection molding machine is high
- Moulds wear out over time and need to be replaced
- The process is slow compared to other manufacturing processes
- Up-front costs can be high for injection moulding, particularly with regard to tooling.
What Are Some of The Considerations For Injection Molding
There are a number of factors to consider when deciding if injection molding is the right manufacturing process for your plastic parts. Some of these factors include:
- The size and shape of the plastic parts
- The number of plastic parts you need to produce
- The material you want to use
- The level of detail you need in your plastic parts
- The strength and durability of the plastic parts
- The finish you need to achieve
- How much the plastic parts will be used
- How it may impact its durability or strength
Our expertise is here to serve you
phone
0086-13564311131
Sales Office: No.29 Moyu Road, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
Shanghai Factory Address: No.998 Huazhi Road, Qingpu District, Shanghai, China
Jiangsu Factory Address: No.777, Jimingtang South Road, Kunshan City, Jiangsu Province
Zhejiang Factory Address: No.1 Xingcheng Road, Yuyao City, Zhejiang Province
Zetar Industry Co.,Ltd
phone
0086-21-64028287


